
Observing how our world has changed from traditional infrastructures to becoming more cloud-based. Yes! We are discussing the omnipresent “cloud.” Cloud computing has been around for almost two decades, and despite statistics showing commercial savings, cost-benefit analyses have never been conclusive. Nevertheless, it has changed how companies communicate, store, and exchange information. It has also changed how they manage computing resources.
Users worldwide access an open pool of resources, including apps, services, servers, data, and computer networks. A privately held cloud or a third-party server makes it possible. It improves data access and eliminates inconsistency in subsequent updates. Additionally, a small amount of administration is necessary.
Before delving into the details, let’s briefly discuss the benefits, challenges, and future trends in cloud computing.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing enables businesses to rent IT resources instead of purchasing them. Rather than making substantial investments in databases, software, and hardware, companies access computing power through the internet, paying only for what they use. These types of cloud computing services encompass various offerings, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and business intelligence.
This model delivers the speed, scalability, and flexibility essential for businesses to develop, innovate, and maintain their IT solutions effectively.
Cloud computing provides modern organizations with cost savings, scalability, flexibility, efficiency, and security. Instead of using internal systems, 70% of our enterprises operate in the cloud. You may have noticed that buying flight tickets or accessing medical records is no longer a Herculean task. That’s all due to the cloud network services.
Cloud services provide flexibility, excellent data storage, improved employee synchronization, and data security. As a result, organizations can make more intelligent decisions about development and growth.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
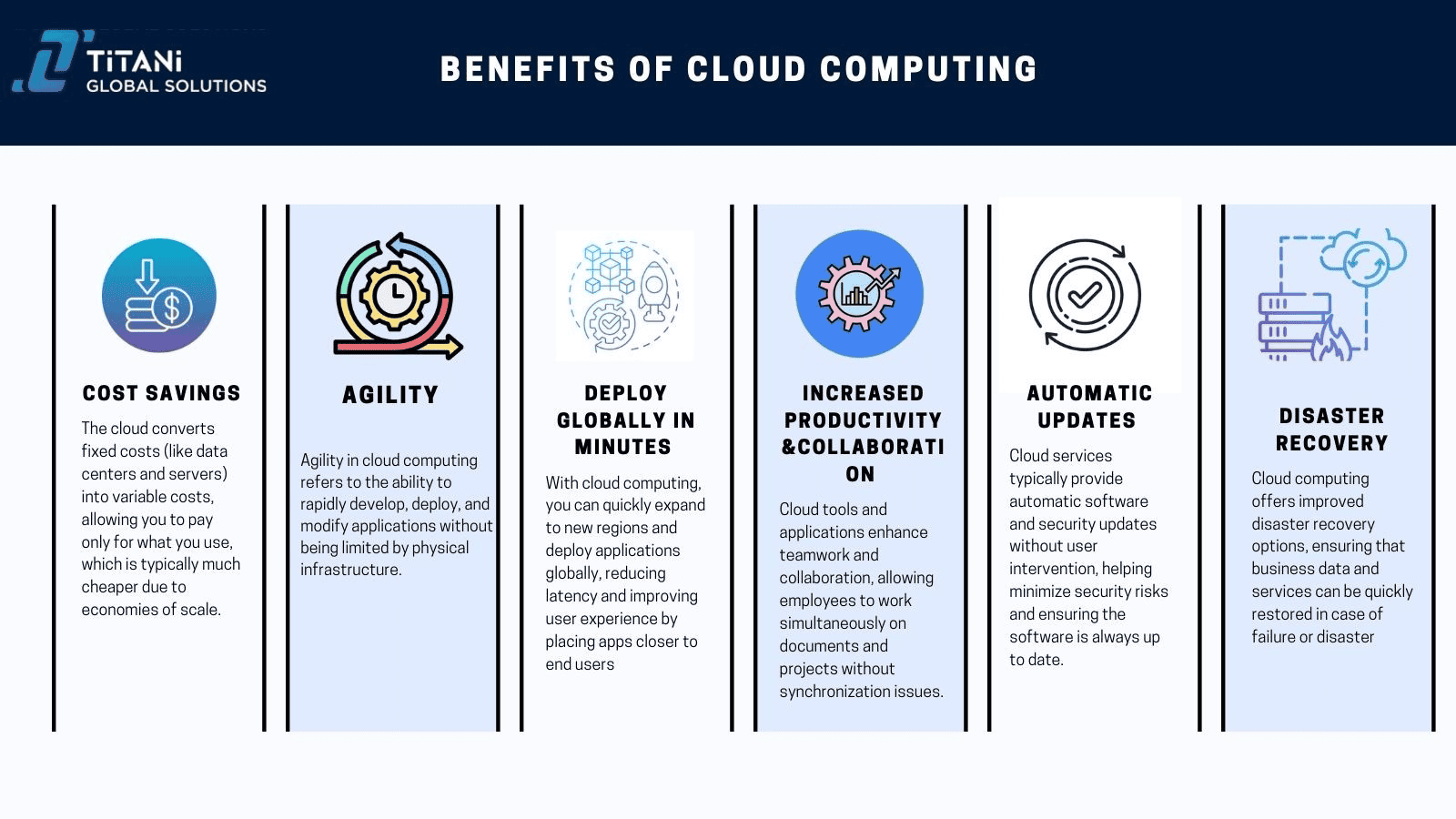
Cost savings
The cloud allows you to trade fixed expenses (such as data centers and physical servers) for variable expenses and only pay for IT as you consume it. Plus, the variable expenses are much lower than what you would pay to do it yourself because of the economies of scale.
Example: A small startup might spend thousands of dollars on physical servers, storage devices, and IT infrastructure. With cloud computing, they can access the same resources for a fraction of the cost.
According to Forbes, 88% of enterprises reported significant cost savings after migrating to the cloud, with many saving up to 40% on IT costs.
Agility
The cloud gives you easy access to a broad range of technologies so that you can innovate faster and build nearly anything that you can imagine. You can quickly spin up resources as you need them–from infrastructure services, such as computing, storage, and databases, to the Internet of Things, machine learning, data lakes, analytics, and much more.
You can deploy technology services in a matter of minutes and get from idea to implementation several orders of magnitude faster than before. This gives you the freedom to experiment, test new ideas to differentiate customer experiences, and transform your business.
Elasticity
With cloud computing, you don’t have to over-provision resources upfront to handle peak levels of business activity in the future. Instead, you provision the number of resources that you need. You can scale these resources up or down to instantly grow and shrink capacity as your business needs change.
Deploy globally in minutes
With the cloud, you can expand to new geographic regions and deploy globally in minutes. For example, AWS has infrastructure all over the world, so you can deploy your application in multiple physical locations with just a few clicks. Putting applications in closer proximity to end users reduces latency and improves their experience.
Increased Productivity and Collaboration
Cloud tools and applications enhance teamwork and collaboration, allowing employees to work simultaneously on documents and projects without synchronization issues.
Example: A multinational marketing agency uses cloud-based tools like Google Workspace and Slack to collaborate on campaigns. Team members from different countries can work on the same document in real-time, update project timelines, and chat seamlessly, regardless of time zone or location. This reduces delays, ensures all team members are on the same page, and speeds up project completion times.
According to a McKinsey report, cloud-based collaboration tools improve productivity by 20-30% by making it easier for teams to share information, communicate quickly, and access data remotely. Salesforce states that cloud-based collaboration tools can improve business processes by 30-50%, enabling faster decision-making, increasing engagement, and boosting overall efficiency.
Automatic Updates
Cloud services typically provide automatic software and security updates without user intervention, helping minimize security risks and ensuring the software is always up to date.
Example: A company using a cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) system like Salesforce automatically receives software updates, ensuring that they always have the latest features and security patches without manual intervention.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) claims that 80% of businesses using its cloud infrastructure benefit from automatic updates and reduced IT maintenance time.
Disaster Recovery
Cloud computing offers improved disaster recovery options, ensuring that business data and services can be quickly restored in case of failure or disaster
Example: A healthcare provider using a cloud platform like AWS or Microsoft Azure stores its patient data in the cloud. In case of a local server failure or natural disaster, the cloud service provider automatically replicates the data to other geographical locations. This ensures that the healthcare provider can continue operations with minimal disruption, accessing patient records securely from any location without data loss.
Gartner reports that 70% of businesses that experience a major data loss due to a disaster go out of business within a year. Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions significantly reduce this risk.
According to a Veeam survey, 92% of businesses that implement cloud disaster recovery see a 50% reduction in downtime after incidents, helping them recover more quickly compared to traditional on-site disaster recovery systems.
Forbes states that 96% of companies that use cloud-based disaster recovery have seen a faster recovery time compared to businesses using on-premise recovery systems.
Cloud Computing Challenges
The cloud is an important resource with many benefits, but it also comes with many risks and challenges. Below we will delve into some of the most common cloud computing challenges facing the industry, cloud security challenges and risks, and common cloud computing problems and solutions.
Data security and privacy
When working with Cloud environments, data security is a major concern as users have to take responsibility for their data, and not all Cloud providers can assure 100% data privacy.
No identity access management, lack of visibility and control tools, data misuse, and cloud misconfiguration are the common reasons behind cloud privacy leaks. There are also concerns about malicious insiders, insecure APIs, and neglect or oversights in cloud data management.
Cost Management
Without significant investments in new hardware, a company can rapidly increase its processing capacity in the cloud trends. Instead, businesses can use public carriers’ pay-as-you-go strategies to get additional processing. Most of the all-cloud providers offer a “pay-as-you-go” model. It brings down the total cost of the resources being used. However, defining and forecasting quantities and costs can occasionally be challenging due to cloud computing services’ on-demand and scalable nature.
Multi-Cloud Environments
Companies now have more options, so they no longer depend on only one cloud provider but several of them. Nearly 84% of these organizations depend on several clouds, most of which employ hybrid cloud strategies. The infrastructure team frequently finds this to be hindering and challenging to manage. The process frequently ends up being extremely complicated for the IT team due to the variations among various cloud infrastructure service providers
Performance Challenges
Performance is a crucial factor when considering cloud-based solutions. If the cloud performs poorly, users may stop using it, and businesses may suffer. For instance, the minimum latency when loading an app or website might cause a significant decrease in the number of users. This latency may result from ineffective load balancing, which indicates that the server cannot divide incoming traffic effectively for the optimal user experience. Fault tolerance, which refers to the ability for operations to continue even when one or more components fail, also presents difficulties.
Portability
Application migration from one cloud provider to another should be simple, but this is another challenge for cloud computing applications. Vendor lock-in must also be avoided. It is not practicable because each cloud provider utilizes a separate standard language for its systems.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing
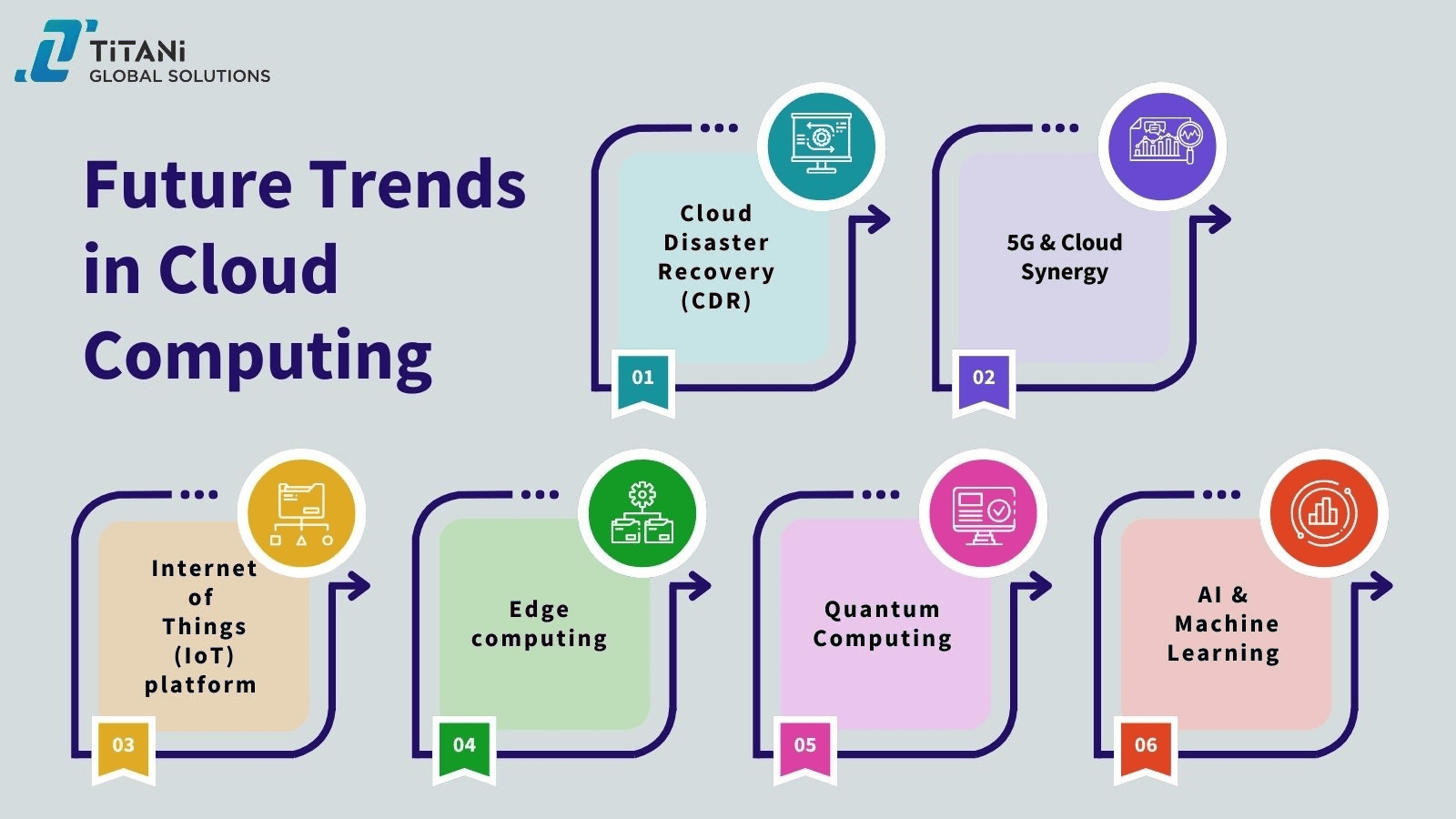
The future of cloud computing is evolving rapidly, with new technologies and trends emerging to further enhance its capabilities. Here are some key trends that will shape the future of cloud computing:
1. Cloud Disaster Recovery (CDR)
Cloud Disaster Recovery (CDR) is a cloud-based backup and recovery solution that helps businesses restore data, applications, and IT infrastructure in case of a disaster. Instead of relying on on-premises recovery systems, CDR leverages cloud resources to provide a fast, scalable, and cost-effective way to recover from failures such as:
Cyberattacks (ransomware, malware, DDoS)
Hardware or software failures
Natural disasters (earthquakes, floods, fires)
Human errors (accidental deletion, misconfiguration)
CDR ensures business continuity by minimizing downtime and data loss through automated backup and rapid recovery.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning Integration
Cloud providers are increasingly incorporating AI and ML into their services, making it easier for organizations to leverage these technologies without needing in-house expertise. AI-powered tools like predictive analytics, natural language processing (NLP), and intelligent automation are already a growing part of cloud offerings.
3. 5G and Cloud Synergy
The rollout of 5G networks will significantly impact cloud computing, especially in areas like IoT, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR). With faster and more reliable connectivity, the combination of 5G and cloud computing will enable ultra-low latency applications and more dynamic data processing.
4. Internet of Things (IoT) platform
An IoT platform is a cloud-based framework that enables connectivity, data collection, processing, and management of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It acts as a bridge between IoT hardware (sensors, devices, machines) and applications, allowing businesses to analyze and act on real-time data.
Key Components of an IoT Platform
Device Connectivity & Management
Data Ingestion & Processing
Security & Compliance
Scalability & Edge Computing
Integration with Cloud & AI Services
5. Edge Computing
Edge computing refers to processing data closer to the source (e.g., IoT devices) rather than relying on centralized cloud data centers. This reduces latency and improves real-time data processing. As IoT devices become more pervasive, edge computing will become integral to cloud infrastructures.
6. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is still in its early stages but is poised to revolutionize industries. Cloud providers like IBM, Microsoft, and Google are making quantum computing accessible through the cloud, enabling research and development without needing massive infrastructure investment.
Conclusion
Understanding why more people use cloud computing every year doesn’t take long. Companies know the advantages, cloud computing industry trends, and challenges of cloud computing implementation and how it impacts their income, security, and teamwork.
Beyond Cloud Computing – Tailored Solutions for Your Business!
Cloud technology is just the start! Enhance your digital transformation with our Custom Software Development services, designed to meet your unique business needs. Whether you're looking to build scalable applications, streamline operations, or optimize performance, we deliver innovative solutions that drive success.
Using cloud platform solutions can help an enterprise avoid issues plaguing companies that rely on on-premises technology, including security issues in cloud computing. If users have any queries about implementing the cloud efficiently for their business, improving cloud performance, or reducing costs, they should contact Titani Global Solutions.