Summary for Decision-Makers
AI adoption in the UAE is accelerating under Vision 2031, with enterprises in finance, healthcare, logistics, and government embedding AI into core operations. However, unlike traditional software, AI models learn, drift, and behave unpredictably, creating risks of bias, compliance breaches, and reputational damage if not thoroughly tested.
AI Testing addresses these risks by validating accuracy, fairness, transparency, and long-term reliability across the full AI lifecycle from data preparation to deployment and monitoring. For UAE businesses, this is especially critical: local regulations demand compliance, customers expect fairness across languages and demographics, and systems must scale quickly without sacrificing trust.
In 2025, AI Testing is not just a safeguard—it’s a strategic enabler. Done right, it ensures that intelligent systems stay reliable, responsible, and growth-ready, turning AI innovation into lasting business value.

Today, artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer futuristic. It’s now a key force behind how businesses run, serve customers, and make decisions. From smart chatbots and fraud detection engines to personalized recommendations and predictive analytics, AI is powering intelligent automation across industries.
Nowhere is this shift more visible than in the UAE, where national strategies like the UAE AI Strategy 2031 are accelerating both public and private investment in AI technologies.
But with rapid adoption comes growing risk.
AI doesn’t work like traditional software. AI learns from data and adapts over time. This flexibility also means it can make mistakes, sometimes in ways that are hard to detect. Left unchecked, these systems may produce biased results, behave inconsistently, or fail silently in critical scenarios.
That’s why AI Testing is no longer optional—it’s essential.
If your business uses or builds AI-powered systems, this guide will help. It explains how testing ensures your models are reliable, trustworthy, and ready for real-world use.
What Is AI Testing?
AI Testing means checking if your AI systems work the way they should in real-world use. These could be models for machine learning, language processing, or product recommendation.
But testing AI isn’t like testing traditional software.
In conventional applications, developers write rules and logic manually. If the code matches the defined rules, developers consider it correct. But AI systems learn from data and adjust their behavior over time. As a result, their logic can shift. Outputs may be unpredictable, and performance can change depending on the data they process.
So instead of just testing whether the software functions, AI Testing focuses on whether the model is making good decisions:
Accurate – Does the model produce correct predictions?
Fair – Does it work consistently across different user groups?
Transparent – Can we explain how and why it made a decision?
Reliable over time – Does it degrade as the data evolves?
This kind of testing looks at more than just whether the code runs. It asks:
“Is the AI behaving responsibly—and will it continue to do so after deployment?”
In short, AI Testing is about testing the AI itself, not using AI as a tool to test other software.
We explain this distinction in more detail in our article on AI-powered testing vs manual QA.
Testing AI is critical for any business using smart systems. This is even more important when those systems affect customers, health, finance, or public services.
How AI Testing Works Across the AI Lifecycle
AI systems don’t come together in a single step. Just like a product or a business strategy, they evolve through multiple stages from idea to deployment, and beyond.
We call this multi-phase journey the AI Software Development Lifecycle, or AI-SDLC. Each stage of AI development needs different types of testing. The goal is to keep the model not only smart but also safe, fair, and reliable.
Here’s how AI Testing fits into each step of the AI lifecycle:
1. Problem Definition
Every AI initiative starts with one important question: What are we trying to solve? At this early stage, AI Testing helps determine whether the problem is suitable for AI in the first place. It also validates whether business expectations are clearly defined, risks are identified, and ethical concerns are addressed early. Testing at this stage ensures you solve the right problem. It helps avoid wasting time on issues that don’t need AI.
2. Data Collection and Preparation
Once the problem is defined, the next step is collecting and preparing the data that the AI will learn from. This is where many failures begin if testing is skipped. AI Testing at this stage focuses on checking the completeness, consistency, and fairness of data. For example, a hiring model trained mostly on data from one gender may show bias. The same risk applies to unbalanced age groups. We also test for data privacy compliance and look out for issues like missing values, incorrect labels, or unbalanced datasets.
3. Model Development and Training
With clean data in hand, the model gets built and trained. Here, AI Testing ensures that the model architecture is appropriate, the training process is stable, and that the model isn’t simply memorizing patterns without truly learning. We check if the model behaves consistently, if results can be reproduced, and whether it starts to overfit, performing well on training data but poorly on anything new.
4. Model Evaluation and Refinement
After training, it’s time to evaluate the model using fresh, unseen data. This is one of the most critical stages for AI Testing. We measure performance not just by accuracy, but also fairness, interpretability, and consistency across demographics. A model that works well for most users but fails for a specific group, like Arabic speakers or older adults, is not ready for production. We also use tools like SHAP and LIME to explain how the model makes decisions, which is vital for auditability and trust.
5. Deployment and Monitoring
Once the model passes evaluation, it’s deployed into a real system. But AI Testing doesn’t stop here. We verify that the model connects properly to your platforms and APIs, returns predictions within an acceptable timeframe, and handles exceptions smoothly. In many cases, we run shadow deployments, where the new model runs silently alongside the old one to test performance before a full launch.
6. Ongoing Maintenance and Drift Detection
AI is never “done.” Models continue to learn or degrade over time as new data comes in. This makes continuous testing essential. We monitor performance trends, detect when the model starts drifting away from its original behavior, and validate whether retraining is needed. A model that was accurate six months ago may now be outdated if customer behavior or market data has shifted. Ongoing AI Testing helps catch that early and keeps your systems sharp and reliable.
Why Businesses in the UAE Need AI Testing
The UAE is quickly becoming one of the world’s most ambitious adopters of artificial intelligence. From smart cities and digital government to healthcare, finance, and logistics, AI is playing a central role in the country’s innovation roadmap. National programs like the UAE AI Strategy 2031 reflect just how serious the country is about becoming a global AI leader.
But as more AI systems move from labs into real-world services, businesses face a growing challenge: how to ensure these systems perform fairly, safely, and reliably under pressure.
One of the most urgent needs in the UAE is compliance. As regulations evolve to govern how AI is deployed, especially in finance, healthcare, and public services, organizations must show that their models are not biased, do not make arbitrary decisions, and do not compromise privacy. Without proper testing, these models could unintentionally violate legal or ethical standards.
Reputation risk is another key concern. In a digitally connected country like the UAE, one faulty AI decision, such as denying customer service, approving the wrong transaction, or producing biased outcomes, can cause lasting damage to public trust. Testing helps uncover these risks early, before they affect your users.
The UAE is also a multilingual, multicultural market, and many AI models trained on Western datasets simply don’t perform well with Arabic text, local dialects, or region-specific behavior. Testing ensures your models are locally relevant, not just globally functional.
Lastly, the UAE’s fast-paced growth means AI systems must scale quickly. But speed without quality is risky. AI Testing gives businesses a structured way to scale their models with confidence, knowing that they’ll continue to perform even as user volumes grow or data shifts.
Whether you’re a government agency deploying AI in citizen services or a private business integrating AI into your customer journey, robust testing is what turns innovation into trust.
Benefits of Using AI Testing
AI may be intelligent, but it isn’t perfect. Like any system built on complex logic and dynamic inputs, AI can go wrong, sometimes quietly, sometimes at scale. Without testing, these errors are often discovered too late: after a customer has been mistreated, a decision has been made unfairly, or a business outcome has been compromised.
This is why AI Testing is becoming an essential part of every AI-driven project, not just to detect problems, but to prevent them.
1. Improve Accuracy and Reliability
One of the most valuable benefits is improving accuracy and reliability. By validating the data that feeds your model and closely monitoring how the model behaves, testing helps ensure that predictions are grounded in logic, not noise or bias. A product recommendation engine, for example, is only useful if it’s learning from clean, complete, and relevant data, not outdated patterns or skewed information.
2. Catch Problems Early
AI Testing also helps businesses catch problems early, before they cause real-world impact. Logic errors, edge-case failures, or performance drops across certain user groups often go unnoticed until it’s too late. With testing integrated across the lifecycle from data prep to post-deployment, issues can be identified and resolved proactively. This approach reduces costs, prevents rework, and protects user experience.
3. Build Trust with Stakeholders
Trust is another critical benefit. Whether you're reporting to regulators, serving diverse customer bases, or simply protecting your brand, AI Testing provides documentation and evidence that your systems behave ethically and predictably. In a world where AI can influence financial approvals, healthcare decisions, or government services, building that trust isn't optional—it’s essential.
4. Optimize Costs and Long-Term Performance
And finally, AI Testing helps optimize costs. While testing may seem like an additional step, it ultimately prevents expensive fixes down the line. By ensuring your models are stable, explainable, and aligned with business goals, you avoid the risk of reengineering entire pipelines, facing public backlash, or losing users to unreliable performance.
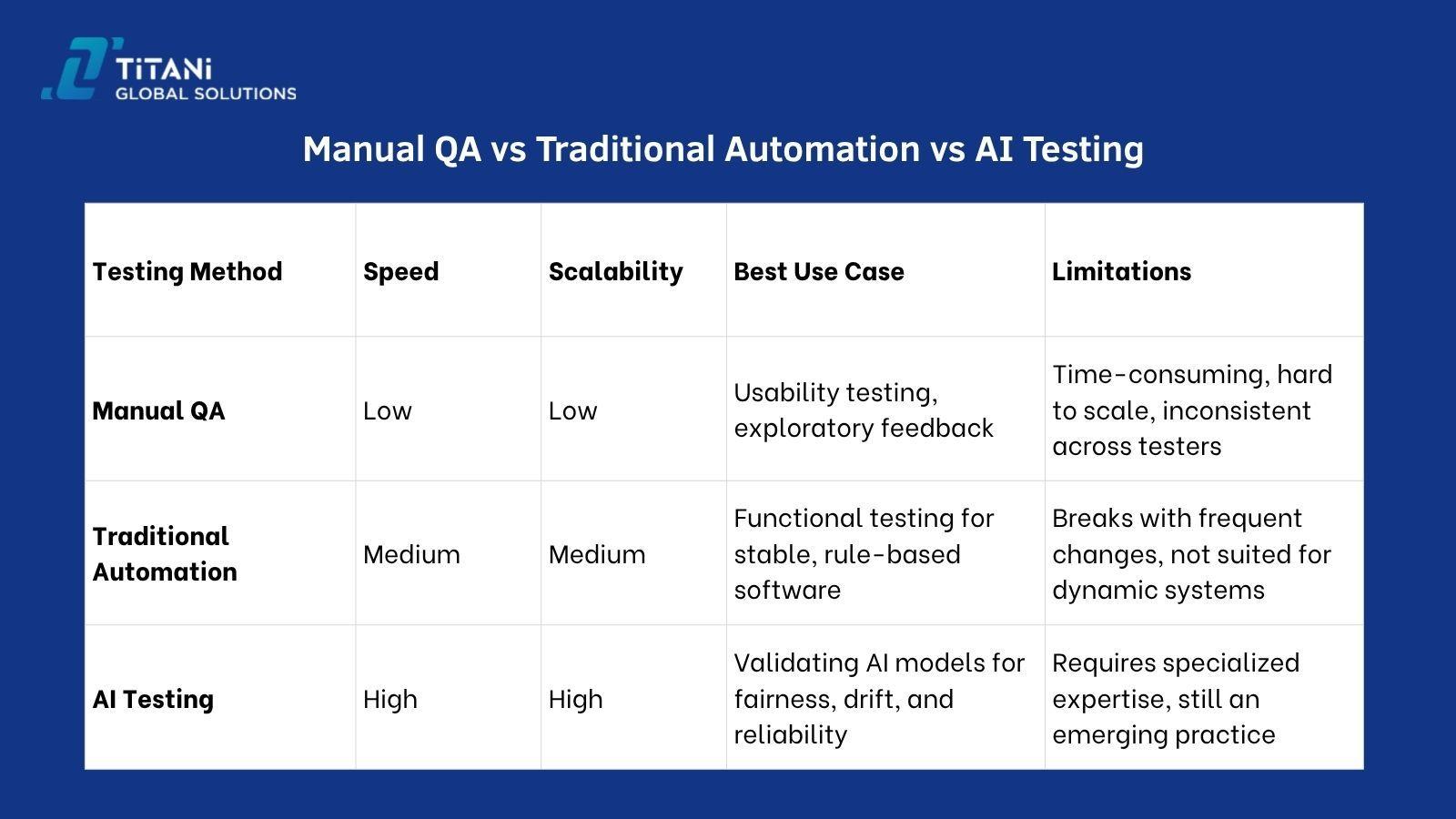
Manual QA vs Traditional Automation vs AI Testing
Not all testing methods work the same. As software becomes more intelligent, the way we test it must evolve as well. Traditional QA methods like manual or scripted testing don’t work well for systems that learn and evolve over time.
To help you understand where AI testing fits in, here’s a breakdown of how it compares with other common testing approaches:
Learn more: AI-Powered Testing vs Manual QA: Which Wins? AI-Powered Testing vs Manual QA: Which Wins?
Why Choose Titani for AI Testing (and What’s Next)
At Titani Global Solutions, we don’t just test software. We help businesses build trust in their most intelligent systems. Whether you’re launching your first AI model or scaling a pipeline, our team supports you at every step with tailored AI Testing.
AI doesn’t behave like regular software, so it needs a different approach to testing. That’s why we focus on checking each model for accuracy, bias, fairness, explainability, and consistent performance over time.
Our team brings deep experience in quality assurance, data science, and software engineering, blending technical precision with real-world business insight. Whether your AI is used in fintech, healthcare, e-commerce, or public services, we tailor our methods to match your needs and regulatory environment.
While we’re still early in our journey in the UAE, we’re actively investing in building local expertise, including support for Arabic language models, region-specific testing standards, and compliance with UAE data and AI regulations. We’re not just a testing provider, we’re a long-term partner in helping you deploy AI that’s safe, responsible, and ready to scale.
If you’re planning to roll out an AI-powered product or just want to ensure the one you have is working as intended, we’d love to help.
👉 Contact us today to learn more about how we can support your AI QA journey.



