Summary
AI in Software Testing is no longer experimental — it has become a core capability for QA teams facing rapid releases, complex systems, and rising quality expectations in 2026.
AI enhances—not replaces—human testers by handling scale, prediction, and maintenance, while humans retain control over strategy, judgment, and user experience.
The real value of AI testing lies in specific capabilities, including predictive risk analysis, intelligent test generation, self-healing automation, visual validation, and anomaly detection.
The most effective QA approach is hybrid: AI-driven testing accelerates coverage and stability, while manual QA ensures usability, ethics, business logic, and trust.
Successful adoption depends on governance and intent, not tools alone—AI improves efficiency, but experienced teams still define quality, manage risk, and make final decisions.

Software teams today are shipping faster than ever, yet quality expectations are rising just as quickly. Modern applications from mobile-first products to AI-driven systems—evolve constantly, making traditional testing harder to maintain and increasingly prone to failure. This is where AI in software testing is fundamentally reshaping the QA landscape.
Beyond manual checks and fragile automation scripts, AI enables teams to predict risks, generate intelligent test scenarios, and self-heal broken scripts at a scale unattainable by human effort alone. For organizations balancing the pressure of rapid releases with the need for rock-solid reliability, AI offers a strategic path to expand coverage, eliminate bottlenecks, and build confidence in every deployment.
This article breaks down how AI-powered testing works, where it delivers the most value, and provides a practical roadmap for safe, transparent adoption—starting small while enabling long-term quality gains.
What Is AI in Software Testing?
At its core, AI in software testing is the strategic integration of intelligent systems to augment the most complex and unscalable aspects of quality assurance: early risk detection, meaningful test creation, and maintaining automation stability in a constantly evolving product landscape. It is not a replacement for human testers; it’s a powerful ally designed to remove the repetitive, brittle, and draining tasks that slow teams down and create bottlenecks in innovation.
Unlike traditional automation that relies on rigid, predefined rules, AI-driven testing learns from real-world patterns. It analyzes code commits, user behavior, historical defect trends, and even subtle visual regressions in the UI. With that context, AI systems can:
Anticipate: Recommend the most critical test cases for a specific code change.
Innovate: Generate edge-case scenarios human intuition may not catch.
Heal: Detect when an interface looks inconsistent—even without an explicit assertion.
For modern QA teams, this fundamentally shifts how quality work gets done. Humans remain the architects of testing strategy and the guardians of user experience, while AI provides the “superpowers” needed to achieve full visibility, reduce maintenance debt, and keep pace with rapid release cycles without burning out.
At Titani Global Solutions, this balanced model of human expertise + AI-driven intelligence is central to how we approach modern QA. Our goal is to help teams adopt AI safely and transparently—enhancing quality, not complexity.
Why AI in Software Testing Is Becoming Critical in 2026
Software delivery continues to accelerate in 2026. Teams ship updates weekly—or even several times per day—while applications become more distributed, data-driven, and increasingly reliant on AI models. This creates a testing environment that traditional methods can no longer scale to support.
Modern QA teams are facing three converging pressures:
1. Products evolve faster than manual or rule-based automation can handle.
A minor UI tweak or API refactor can break dozens of scripts overnight. Maintenance consumes time and energy, leaving little capacity for exploratory or risk-based testing.
2. User expectations for reliability are higher than ever.
Any disruption in checkout flows, onboarding journeys, or customer support interactions can translate directly into lost revenue and damaged trust.
This shift is no longer speculative. According to Gartner, AI-driven testing has moved beyond experimentation and into mainstream QA practices, helping teams prioritize risk, stabilize automation, and accelerate release cycles.
Entering 2026, this reflects a broader reality: software quality is now a competitive differentiator, not just an engineering concern.
3. Engineering teams must do more with fewer resources.
Release cycles shrink, but expectations around coverage, traceability, and compliance keep growing. Without additional intelligence, QA teams are forced into a constant trade-off between speed and safety.
This is where AI in software testing moves from “interesting experiment” to core capability. AI can analyze change patterns immediately, prioritize the tests that matter most, uncover risks earlier, and keep automation stable even as the product shifts day by day.
Core Capabilities of AI in Software Testing
AI in Software Testing isn’t a single feature or tool. It’s a set of intelligent capabilities designed to address the most persistent pain points in modern QA—areas where traditional automation struggles to scale or adapt.
When applied thoughtfully, these capabilities make testing more resilient, less script-dependent, and far better suited to fast-changing products.
1. Predictive Test Analytics: Focusing on What Matters Most
One of the most practical advantages of AI is its ability to predict risk. Instead of treating all features equally, AI analyzes historical defects, code changes, and production incidents to identify which areas are most likely to fail.
For example, if a specific service frequently breaks after refactoring, AI can automatically raise its priority during regression testing. This helps QA teams spend their time where it has the greatest impact, rather than running broad test suites just to feel “covered.”
2. Intelligent Test Case Generation: Going Beyond Happy Paths
AI can assist in generating test cases directly from requirements, user flows, or real usage patterns. More importantly, it helps uncover edge cases—unusual conditions or combinations that human testers may not immediately think of.
In complex systems such as e-commerce platforms, financial applications, or multi-role SaaS products, this capability significantly improves coverage without increasing manual workload.
3. NLP-Based Test Authoring: Making Tests Easier to Create and Maintain
With Natural Language Processing (NLP), test cases can be written in clear, business-friendly language—such as “User logs in, updates their profile, and confirms the changes.” AI then translates these steps into executable test scripts.
This approach reduces reliance on coding skills, improves collaboration between QA, product, and business teams, and makes test cases easier to review and update as requirements evolve.
4. Self-Healing Automation: Reducing Maintenance Overhead
Test maintenance is one of the biggest hidden costs of automation. Even small UI changes—renamed elements, shifted layouts—can cause widespread test failures.
Self-healing automation uses AI to detect these changes and automatically adjust locators or flows. While it doesn’t eliminate maintenance entirely, it dramatically reduces the time QA teams spend fixing broken scripts after routine updates.
5. Visual and UX Testing with AI
AI-driven visual testing goes beyond pixel comparison. It understands layout structure and visual intent, allowing it to detect issues such as misaligned elements, clipped text, or inconsistent rendering across devices and browsers.
This is especially valuable for customer-facing applications where visual quality directly affects trust, usability, and conversion rates.
6. Anomaly Detection During Test Execution
Beyond simple pass-or-fail results, AI can identify anomalous behavior during test runs—such as unusual response times, unexpected logs, or patterns that deviate from previous executions.
These signals may not break a test immediately, but they often point to underlying issues that could surface in production if left unchecked.
Taken together, these capabilities shift testing from a rigid, script-driven activity to a more adaptive and insight-led process. At Titani, the strongest results come from introducing these capabilities incrementally—solving specific QA challenges first, then expanding as teams gain confidence and maturity.
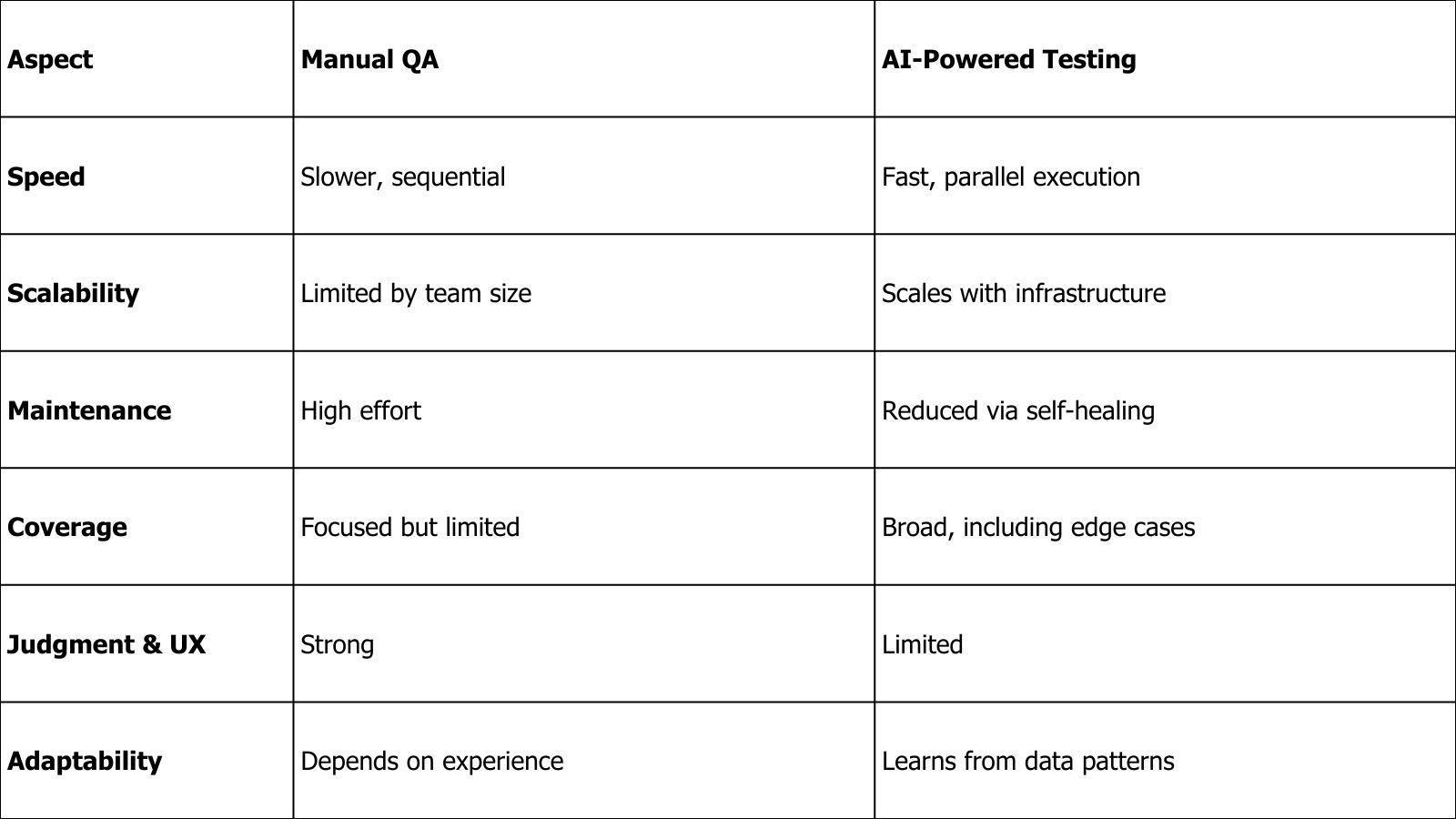
AI-Powered Software Testing vs Manual QA: A Balanced Comparison
Discussions around AI in software testing often frame it as a replacement for manual QA. In practice, this is rarely the goal and almost never the most effective outcome. The real value comes from understanding where AI excels, where humans remain essential, and how the two work best together.
Where AI-Powered Testing Delivers the Most Value
AI brings clear advantages in areas that are repetitive, data-heavy, or difficult to scale manually:
Speed and scalability: AI can execute tests in parallel across environments and prioritize what to test first based on risk.
Consistency: Unlike humans, AI applies the same logic every time, reducing variance caused by fatigue or oversight.
Maintenance reduction: Self-healing capabilities significantly lower the effort required to keep automation stable as applications evolve.
Pattern recognition: AI can spot trends, anomalies, and regressions across large test datasets that would be impractical to analyze manually.
For fast-moving products, these capabilities make the difference between QA being a bottleneck and QA being an enabler.
Where Manual QA Still Matters and Always Will
Despite its strengths, AI has important limitations. Human testers remain critical in areas where judgment, empathy, and context are required:
Exploratory testing: Discovering unexpected behaviors, usability issues, or edge cases that don’t follow predictable patterns.
User experience validation: Assessing whether a product feels right—something AI cannot fully interpret.
Business logic and domain understanding: Evaluating complex workflows, regulatory rules, or industry-specific requirements.
Ethical and risk-based decisions: Especially important when testing AI-driven features that affect users directly.
Manual QA provides the intuition and critical thinking that AI simply cannot replicate.
A Side-by-Side View
The Real Answer: Hybrid QA
The most effective teams don’t choose between AI and manual testing—they combine them. AI handles scale, repetition, and prediction. Humans focus on strategy, experience, and decision-making.
How AI Supports Each Phase of the QA Lifecycle
AI in Software Testing delivers the most value when it supports the QA lifecycle end to end—not by replacing existing practices, but by adding intelligence where traditional methods struggle to scale.
Planning: AI analyzes historical defects, code churn, and production incidents to highlight high-risk areas early, enabling data-driven test prioritization instead of broad, unfocused coverage.
Test Design: By learning from requirements and real usage patterns, AI helps generate relevant scenarios and uncover edge cases, while human testers retain control over validation and intent.
Test Execution: AI prioritizes and adapts test execution based on recent changes, surfacing meaningful anomalies rather than overwhelming teams with raw pass/fail results.
Maintenance: Self-healing automation reduces breakage caused by routine UI or locator changes, lowering maintenance effort without removing human oversight.
Reporting & CI/CD: AI turns test data into actionable insights, supporting faster feedback loops in CI/CD pipelines and helping quality signals influence release decisions.
Practical Use Cases: Where AI in Software Testing Delivers the Most Impact
AI in Software Testing creates the most value when applied to areas where manual effort and traditional automation struggle to keep up with speed, change, and complexity. Instead of spreading AI thinly across all tests, high-performing teams focus on a few critical scenarios.
High-Change Applications and Rapid Release Cycles
Products with frequent UI updates, A/B experiments, or continuous feature releases often suffer from fragile automation and growing regression effort. AI helps teams adapt by prioritizing tests affected by recent changes and stabilizing automation through self-healing mechanisms. The result is faster releases without sacrificing confidence.
Revenue-Critical User Flows
Checkout journeys, onboarding processes, account management, and customer-facing interactions directly impact revenue and trust. AI-driven testing expands coverage around these high-risk paths, detects subtle visual or behavioral regressions, and flags anomalies early—reducing costly failures in production.
Testing AI-Powered Features and Intelligent Systems
As products increasingly embed AI components such as chatbots, recommendation engines, or decision-support logic, traditional deterministic testing falls short. AI-assisted testing helps monitor behavior consistency, detect output drift, and surface unexpected responses, while human testers assess accuracy, tone, and safety.
The Limits of AI in Software Testing: Where Human Judgment Still Matters
AI Depends on Data Quality
AI learns from historical data. When that data is incomplete, biased, or outdated, its recommendations can be inaccurate. In early-stage products or new features, AI often lacks enough context to be reliable on its own.
False Positives and Overconfidence Are Real Risks
AI can flag issues that don’t matter—or miss problems that require domain understanding. Without human review, teams risk trusting results that look confident but aren’t meaningful.
User Experience Still Requires Human Insight
AI struggles to judge whether something feels intuitive, fair, or trustworthy. UX quality, tone, and emotional impact remain areas where human testers are essential.
Ethics, Bias, and Safety Can’t Be Automated Away
For AI-powered features like chatbots or recommendations, humans must assess bias, intent, and potential harm. These decisions require judgment, not pattern matching.
Compliance and Transparency Matter
In regulated environments, teams must explain why tests passed or failed. Some AI tools lack clear traceability, making human oversight critical for audits and governance.
AI Still Needs Direction
This perspective is reinforced by industry research. The World Quality Report consistently emphasizes that while AI improves efficiency and scale, sustainable quality outcomes still depend on human judgment, governance, and organizational maturity.
In other words, AI amplifies quality efforts—but experienced teams remain accountable for defining what “good” actually means.
The Future of AI in Software Testing
AI in Software Testing is moving beyond execution speed toward test intelligence and risk awareness. Instead of relying on static regression suites, QA teams increasingly use AI to decide what to test based on real change patterns, usage data, and historical failures.
As more products embed AI components such as chatbots, agents, and recommendation logic, testing must also validate behavior, consistency, and safety over time. These challenges go beyond what traditional testing can handle alone.
What remains constant is the need for human judgment. AI enhances visibility and reduces maintenance effort, but people still define quality, assess risk, and make final decisions.
At Titani, we help teams adopt AI testing pragmatically—starting with real QA pain points and expanding only where it delivers clear value.
If you’re exploring how to apply AI in testing without overcomplicating your process, you can contact Titani Global Solutions to discuss practical next steps based on your current systems and goals.


